The acceleration due to gravity is constant which means we can apply the kinematics equations to any falling object where air resistance and friction are negligible.
Physics equation for falling off a roof.
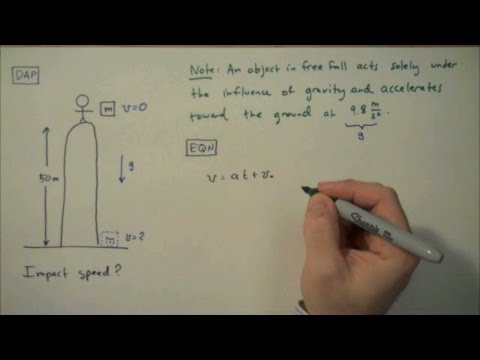
Since there is only the gravitational force pulling down the dude will have a vertical acceleration of negative g where g 9 8 n kg or 9 8 m s 2 if i call.
Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another.
From the definition of velocity we can find the velocity of a falling object is.
If values of three variables are known then the others can be calculated using the equations.
V v gt.
The formula can easily be extended to calculate the approximate maximum impact force a k a.
So let s say that the height is i don t know let s say the height is 5 meters which would be probably jumping off of a or throwing a rock off of a one story maybe a commercial one story building.
The predictability of this acceleration allows one to predict how far it will far or how fast it will be going after any given moment of time.
Peak impact force by multiplying the resulting average impact force by two.
Free falling objects are falling under the sole influence of gravity.
This page describes how this can be done for situations involving free fall motion.
G is the free fall acceleration expressed in m s or ft s.
V is the initial velocity measured in m s or ft s.
Without the effect of air resistance each object in free fall would keep accelerating by 9 80665.
Let s look at this y motion first.
The acceleration of free falling objects is therefore called the acceleration due to gravity.
T stands for the fall time measured in seconds.
The above equation can be used to calculate both impact force of a falling ojbect as well as impact force of a horizontally moving object such as in a car crash or plane crash.
This force causes all free falling objects on earth to accelerate downward towards the earth at a predictable rate of 9 8 m s s.
Each equation contains four variables.
In practice the simplest method for determining the falling object force is to use the conservation of energy as your starting point.
A set of equations describe the resultant trajectories when objects move owing to a constant gravitational force under normal earth bound conditions for example newton s law of universal gravitation simplifies to f mg where m is the mass of the body.
This opens a.
So yeah about the roof of a commercial building give or take.
Well let s try it out with something.
The variables include acceleration a time t displacement d final velocity vf and initial velocity vi.
The force of gravity causes objects to fall toward the center of earth.